Guidelines for the Assessment and Educational Evaluation of Students Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing
Early Intervention
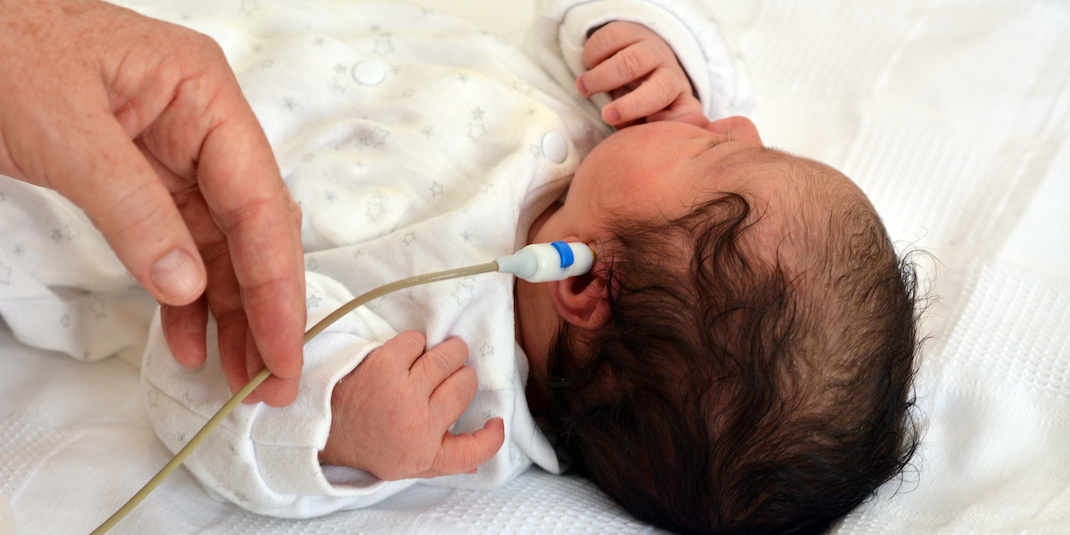
The Universal Newborn Hearing Screening (UNHS) legislation enacted in 2000 created the opportunity for very early identification of hearing levels in infants, leading to earlier family support and the development of communication and language, as needed. As a result of these efforts, many of the students who are D/HH, given appropriate early intervention services, are arriving in our schools with language and communication commensurate with that of their hearing peers.
By contrast, prior to 2000, the average age of identification was 2.5 years of age, leading most educators to spend the early years focusing on closing a significant language gap. While not every student is identified early and begins receiving early intervention, that is our goal for all students.
Ohio’s Early Intervention (EI) services support the physical, cognitive, social, and emotional development of children with disabilities from birth to age three. Birth to age 3 is a window in which a child’s brain is growing a foundation for future life skills and learning. Children who are deaf and hard of hearing may need additional support to develop these foundations.
Teams are encouraged to explore the MedEd Connection Resource Guide: Deaf and Hard of Hearing to build their understanding and connection important medical and educational information to make more informed decisions. This resource guide is designed to support families as they manage, access, and share medical and educational information so that their children who are deaf or hard of hearing (D/HH) can grow and live their best lives.